Automatically segmenting and describing the human corpus callosum from brain MRIs
Description
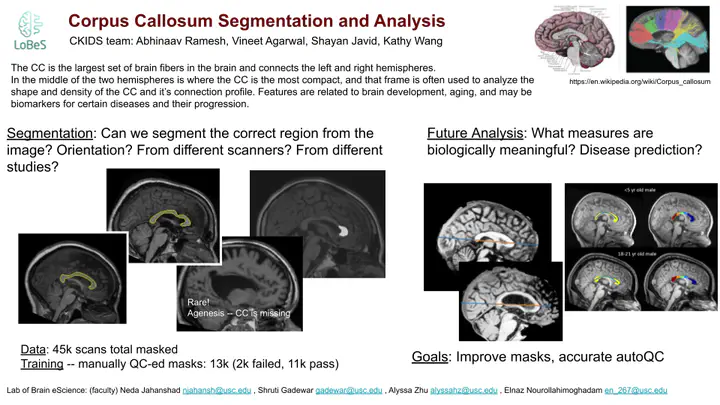
The human corpus callosum is the largest pathway connecting the left and right hemispheres of the brain. The shape of the corpus callosum (CC) changes throughout the course of human development, and it can also be altered with respect to disease onset. We can explore the variation in CC shape along the middle of the brain, but we need to extract it reliably first. The lab currently has two methods for extracting the CC, one using only image processing techniques, and another using deep learning (UNet) but these methods do not always extract the CC accurately. The accuracy results often depend on the MRI scanner that was used, or the abnormalities present in the scan. Can we improve the performance of our deep learning model with additional training data? Can we change some processing steps to improve the model? Once we do have an accurate segmentation, then what shape metrics of the CC as a whole, or in parts, are most telling of the underlying biology, such as age and risk for disease?
Awards
Best Interdisciplinary Data Science Project
Best Project Achievement
Best Project Website
Highlighted Project
Students
Advisors
Skills Required by the team
- Python
- Deep Learning
- Bash
- R